Histology of endometriosis-associated ovarian carcinomas
 Affiliacja i adres do korespondencji
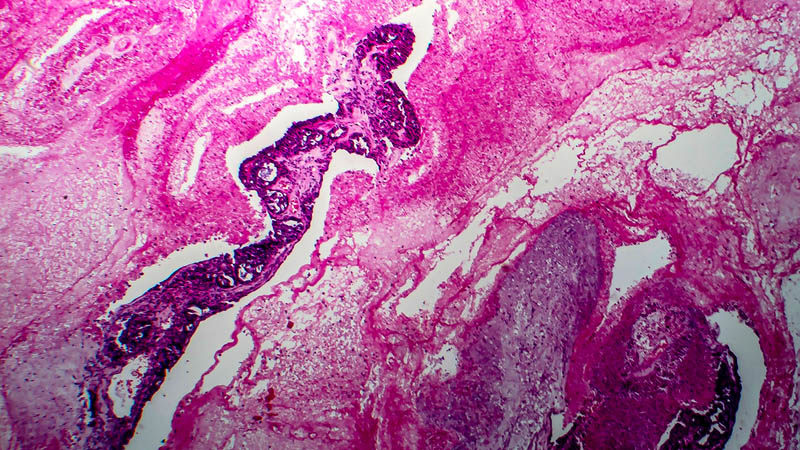
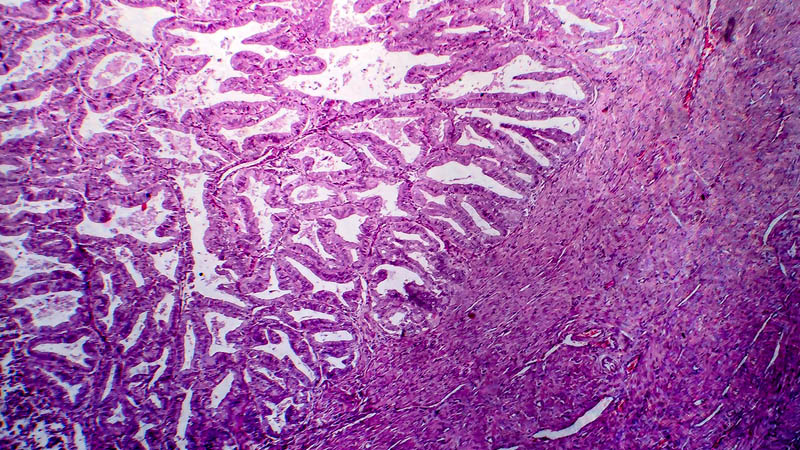
Affiliacja i adres do korespondencjiObjective: The objective of this study was to demonstrate the histological diversity of endometriosis-associated ovarian carcinoma. Material and methods: Using record linkage techniques, we have conducted histopathological assessment in patients with endometriosis-associated ovarian cancer who received surgical treatment between 2004–2010 in the Oncology Centre in Bydgoszcz. Endometriosis and cervical carcinoma were confirmed in one tissue specimen in 62 patients. Results: Endometriosis seemed to promote the development of specific histologic types of ovarian cancer. Of 62 subjects, 53.22% (33/62) had endometrioid adenocarcinoma, 25.8% (16/62) had clear-cell carcinoma, 19.35% (12/62) had serous adenocarcinoma, and 1.61% (1/62) had mucinous adenocarcinoma. Our results support the hypothesis that coexistent endometriosis is more often associated with endometrioid and clear-cell carcinomas than other histologic subtypes as well as that clear-cell variant is the most common cancer developing in the abdominal wall scar from a previous laparotomy. Among patients with endometriosis-associated ovarian carcinoma in the abdominal scar, three (75%) had clear-cell carcinoma and one had papillary serous adenocarcinoma. Conclusions: According to Sampson’s criteria, endometrioid carcinoma of the ovary was the most common histological diagnosis in patients with endometriosis-associated ovarian carcinoma. The clear-cell variant of cancer was the most common type in patients with endometriosis-associated ovarian carcinoma in the abdominal scar after laparotomy.