Type I and II endometrial cancer – a new look at the etiology and clinical course
Anna Markowska1, Monika Pawałowska2, Małgorzata Korcyl1, Janina Markowska2
 Affiliacja i adres do korespondencji
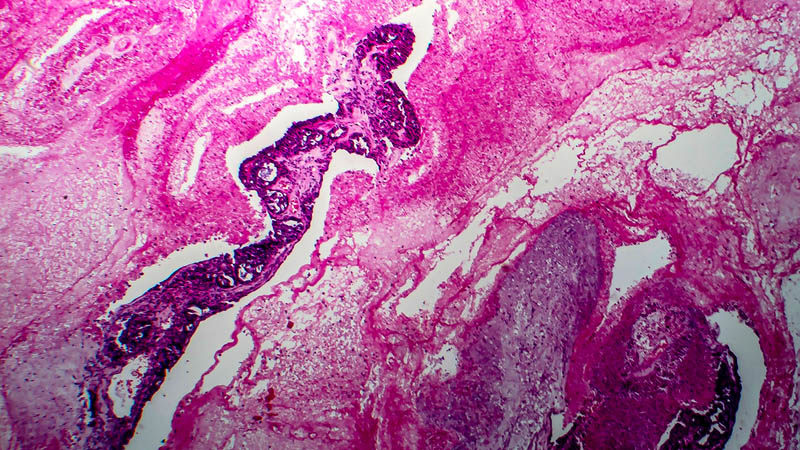
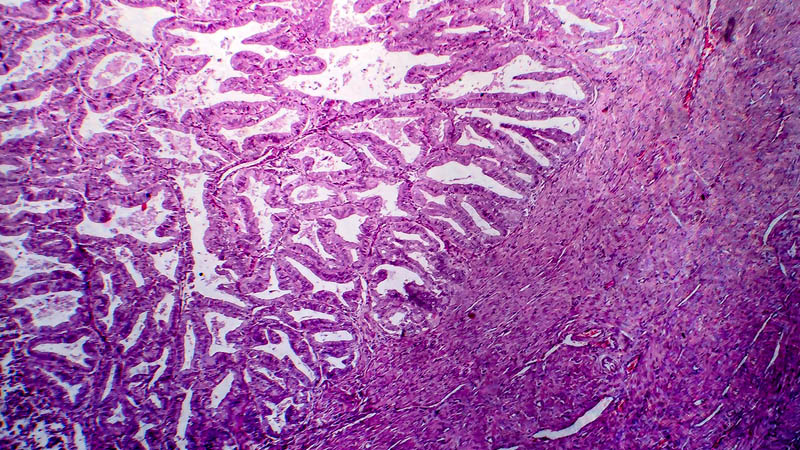
Affiliacja i adres do korespondencjiEndometrial cancer is the most frequent malignancy of female genital organs in more developed countries. It is a heterogeneous tumor with variable risk factors, precancerous conditions, clinical course and prognosis. The majority of cases are sporadic, however endometrial cancer develops in around 8–12% of women with Lynch syndrome, who are at increased risk of this disease. MLH1, MSH2 and MSH6 mutations are observed with equal frequency. Recent molecular studies on endometrial cancer indicate that the classic division into two types according to Bokhman is insufficient, particularly with respect to type II which is less common, and which includes both serous carcinomas and clear-cell carcinomas. Endometrial intraepithelial carcinoma is considered a precursor lesion for uterine serous carcinoma. In immunohistochemical tests (p53, Ki67, ER and PR) it resembles a precursor lesion for ovarian serous carcinoma, possibly indicating the clonal origin of both carcinomas. It is possible that cells from the foci of endometrial intraepithelial carcinoma migrate to the fallopian tube and lead to the peritoneal spread of the disease. Differential diagnosis of uterine serous carcinoma and ovarian serous carcinoma is difficult; testing ER and PR profiles and evaluation of WT1 expression can prove helpful. In recent years, it has been found that uterine serous carcinoma can be associated with the carrier state of mutated BRCA1. These studies are significant since in carriers of mutated BRCA1, apart from prophylactic adnexectomy, hysterectomy should be considered as well. Another important aspect in such cases is therapy with PARP inhibitors.