Genital malignant tumors and precancerous conditions in female carriers of constitutional BRCA1 gene mutations undergoing prophylactic adnexectomy
Janusz Menkiszak1, Anita Chudecka-Głaz1, Ryszard Bedner1, Jacek Gronwald2, Małgorzata Wężowska1, Zbigniew Kojs3, Izabella Rzepka-Górska1
 Affiliacja i adres do korespondencji
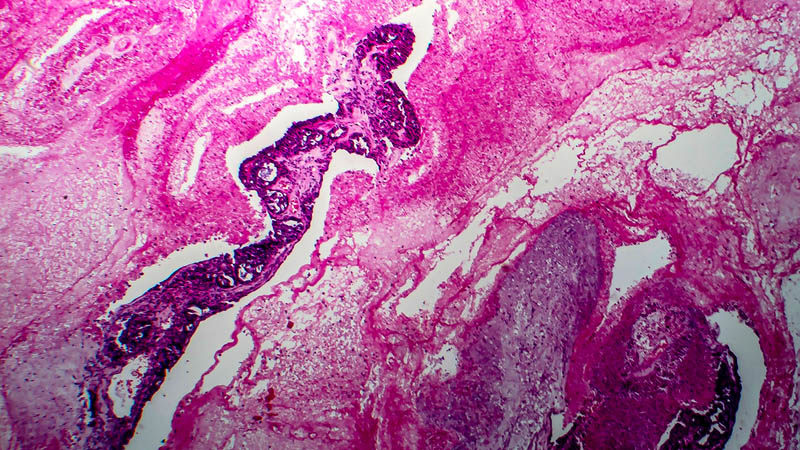
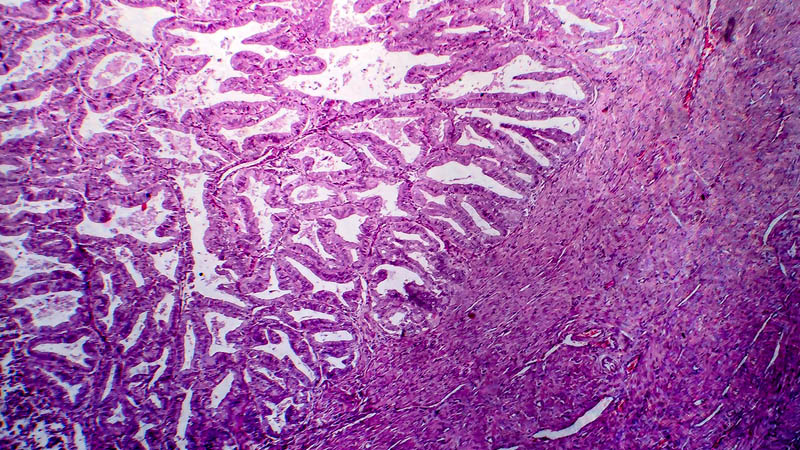
Affiliacja i adres do korespondencjiAim of paper: Assessment of incidence of genital malignant tumors and precancerous conditions in females undergoing prophylactic PBSO/RRSO surgery (prophylactic bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy/risk reducing salpingo-oophorectomy). Material and methods: Study population consisted of 209 women affected with one of three BRCA1 gene mutations most common in the Polish population (5382insC, 4153delA and C61G), undergoing prophylactic genital resection. Procedures were performed in asymptomatic patients and unremarkable findings in ancillary diagnostic tests. Surgeries have been performed over 11 years (since 15.09.1999 thru 31.12.2010). Analysis included number and type of malignant tumors and precancerous conditions detected at surgery as well as patients’ age at the time of diagnosis, compared with mean age of all patients in the study group. Assessed parameters included oncologic data, e.g. clinical stage, histological diagnosis, histological type and morphological malignancy grade correlated with type of constitutional mutation of the BRCA1 gene. Suggested surgery has been accepted by 81.96% (209/255) of the patients. Mean interval between consent for surgery and its execution was 13.27 months (median 4 months). Mean patients’ age at the time of preventive surgery was 48.21 years (median 49 years). In 88.99% of the cases (185/209) adnexectomy was expanded to include the uterine corpus (sparing of the cervix) or the entire uterus. Positive history of oncologic surgery was obtained in 42.11% of the cases (88/209), thereof 40.67% (85/209) operated on due to breast cancer. Results: Histological study of surgical specimens revealed the following oncologic conditions: 8 cases of asymptomatic ovarian cancer, 2 cases of primary peritoneal cancer and 2 cases of primary fallopian tube cancer (12/209 – 5.74%). Thereof, 6 ovarian cancers were at FIGO stage I and 2 at FIGO stage II. One case of asymptomatic endometrial cancer and one case of CIN3 (carcinoma in situ) cervical cancer was detected. Intraepithelial neoplasia (dysplasia) within the fallopian tubes was detected in 8.13% (17/209) of the patients. Overall, early forms of malignant tumors were detected in 7.18% (15/209) of the patients. Most cancers (73%; 11/15) were poorly differentiated (G3) of the serous type. No cases of FIGO stage III and IV disease were noticed. Most patients (62.5%) with malignant tumors and precancerous conditions harbored the insC5382 mutation. Only a single case of cancer has been diagnosed in a patient under 45 – 6.67% (1/15). Conclusions: 1) Prophylactic surgery enables detection of early clinical stages of malignant tumors in female carriers of constitutional mutations of the BRCA1 gene. 2) Preventive genital resection in female carriers of BRCA1 gene mutations is an effective way to detect asymptomatic forms of genital malignancy. 3) Fallopian tube intraepithelial neoplasia (dysplasia) is a relatively frequent condition seen at preventive surgery in BRCA1 gene mutation carriers. 4) Scope of preventive genital tract resection must be tailored depending on individual patient’s situation.