Histopathological diagnosis of endometrial hyperplasia. Part II
Anna Nasierowska-Guttmejer1, Wiesława Grajkowska2, Krzysztof Bardadin3
 Affiliacja i adres do korespondencji
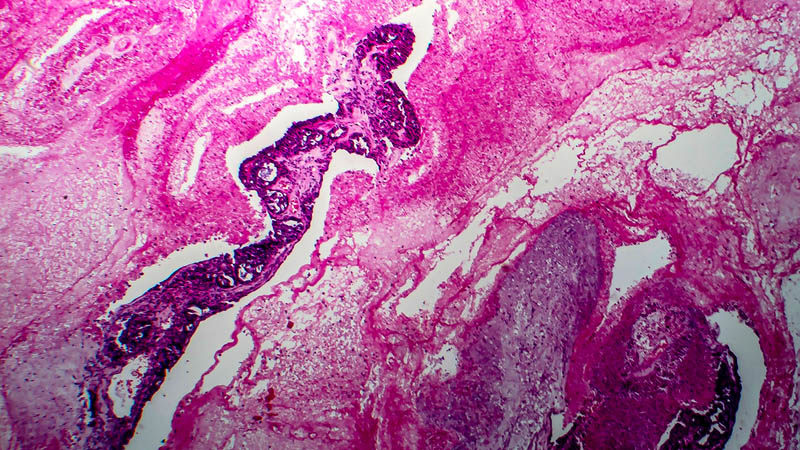
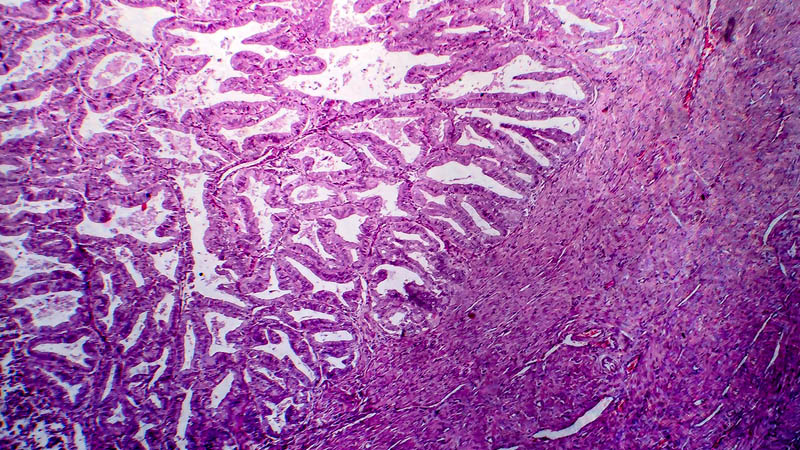
Affiliacja i adres do korespondencjiEndometrial cancer constitutes a heterogeneous group of diseases, in terms of clinical course, underlying molecular disorders, morphology and therapeutic strategy. The most frequent variety is type I or endometrioid cancer. As compared with type II, or non-endometrioid cancer, it usually develops in younger women as a result of prolonged estrogen stimulation within endometrium with features of atypical hyperplasia or a condition defined as endometrial intraepithelial neoplasia (EIN). In terms of morphology, it usually forms an exophytic (rarely endophytic) tumor and presents a high or moderate grade of differentiation. Patients usually present at an initial stage of the disease, with tumor infiltrate rarely exceeding half of uterine wall thickness; lymph node metastases are rare too. Non-endometrioid cancer usually affects older women, where it develops within a flat, atrophic endometrium with no signs of hyperplasia. It is always qualified as poorly differentiated and according to WHO classification its degree of differentiation is not graded. It usually presents an aggressive clinical course, infiltrating over one half of uterine wall thickness, invades the serous membrane and regional lymph nodes. Types I and II of endometrial cancer differ also in terms of underlying molecular disorders. Type I is associated with mutations of genes K-ras, PTEN and MLH1 (DNA repair). Type II is associated with mutation of TP53. The key issue in developing therapeutic strategy is microscopic assessment of type and grade of histological maturity, as well as clinical-pathological stage of cancer. An important issue is to apply currently valid WHO, TNM and FIGO classifications. Objective difficulties in interpretation of microscopic features in some cases result in increasingly frequent use of molecular and immunohistochemical studies in routine pathological diagnostic work-up.